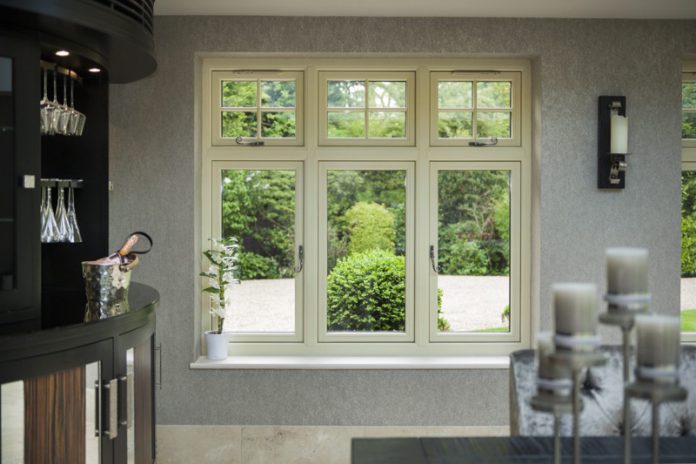
Windows play a crucial role in the comfort and energy efficiency of our homes. Beyond their aesthetic appeal, windows are vital components that contribute to insulation, noise reduction, and overall well-being.
As the quest for energy efficiency and comfortable living spaces continues, the realm of home improvement has witnessed significant advancements in various aspects of construction and design.
Among these, the evolution of window pane options stands out as a pivotal contributor to both aesthetics and functionality.
The journey from single to double glazing has revolutionized the way we view and experience windows, redefining the very essence of natural light, insulation, and sound control within our homes.
This comprehensive guide delves into the world of window installation, focusing on the transition from traditional single glazing to the innovative realm of double glazing.
By unraveling the intricacies of these window pane options, we embark on a voyage that not only enhances energy efficiency but also elevates the overall comfort and value of our living spaces.
Importance of window panes in energy efficiency and comfort
The importance of window panes in energy efficiency and comfort cannot be overstated, as they play a vital role in shaping the indoor environment of a home.
Window panes are not just transparent barriers; they act as a dynamic interface between the interior and exterior, impacting factors such as temperature regulation, natural light penetration, and even noise control.
Homeowners frequently report a noticeable enhancement in comfort after upgrading their windows. With advanced window installations like double glazing, indoor temperature fluctuations are minimized, resulting in a more stable and comfortable living environment. Testimonials often mention the elimination of drafts, cold spots, and uneven heating or cooling, leading to a cozier and more enjoyable indoor space.
Understanding the significance of window panes in relation to energy efficiency and comfort involves considering several key aspects:
Thermal Insulation
Window panes serve as a barrier between the indoor and outdoor environments, influencing the transfer of heat.
Inefficient or single-pane windows can lead to significant heat loss during colder months and heat gain during warmer months. This can result in increased energy consumption for heating and cooling systems, leading to higher utility bills and reduced comfort.
Natural Light
Properly designed window panes allow natural light to enter the interior spaces, reducing the need for artificial lighting during daylight hours. This not only contributes to energy savings but also enhances the overall comfort and well-being of occupants by providing a connection to the outdoors and promoting a visually pleasing environment.
Solar Heat Gain
The type of glass and coating used in window panes can influence the amount of solar heat that enters a building.
Selecting the right window pane options can help regulate solar heat gain, reducing the need for excessive cooling in warmer months and contributing to a comfortable indoor temperature.
Noise Control
Well-designed window panes can also play a role in minimizing outdoor noise infiltration, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment. This is particularly important for homes located in noisy urban areas or near busy streets.
Condensation Control
Double glazing and advanced window pane technologies help mitigate condensation by maintaining a warmer inner pane temperature, reducing the likelihood of moisture buildup and potential damage to window frames and surrounding areas.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Impact
The energy efficiency of window panes directly impacts a home’s carbon footprint. By choosing energy-efficient window panes, homeowners can contribute to a reduced environmental impact by decreasing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Exploring Single Glazing
Single glazing, a traditional window pane option, has been a longstanding choice in architectural design. It consists of a single sheet of glass that serves as a barrier between the indoor and outdoor environments.
While single glazing has historical significance and aesthetic appeal, it’s important to understand its characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and its impact on energy efficiency and comfort.
Single glazing is characterized by its simplicity. It typically consists of a single pane of glass set within a window frame. This basic design allows for unobstructed views and lets natural light enter indoor spaces without significant interference.
Advantages of Single Glazing
Aesthetic Appeal
Single glazing can offer a classic, timeless appearance that complements certain architectural styles and design preferences.
Affordability
In terms of initial cost, single glazing is often more budget-friendly than more advanced window pane options.
Historical and Vintage Charm
Single glazing is commonly found in historical and vintage buildings, contributing to their unique character and preserving their original design.
Disadvantages of Single Glazing
Limited Insulation
Single glazing provides minimal insulation against temperature variations, which can lead to heat loss during cold months and heat gain during hot months. This can result in higher energy bills and reduced indoor comfort.
Poor Noise Control
Single glazing offers limited noise reduction capabilities, allowing outdoor sounds to penetrate indoor spaces more easily.
Condensation Issues
Single glazing is more prone to condensation, particularly in cold weather. Condensation can lead to moisture-related problems such as mold growth and deterioration of window frames.
Energy Inefficiency
Due to its limited insulation properties, single glazing contributes to higher energy consumption and may not meet modern energy efficiency standards.
Impact on Energy Efficiency and Comfort
Single glazing’s minimal insulation properties directly impact energy efficiency and comfort. Its inability to effectively regulate indoor temperatures can lead to drafts, uneven heating or cooling, and a less comfortable living environment.
Additionally, the lack of adequate insulation can strain heating and cooling systems, leading to increased energy consumption and higher utility bills.
The Evolution to Double Glazing
The evolution from traditional single glazing to the modern innovation of double glazing marks a significant advancement in window pane technology. Double glazing, also known as insulated glazing, involves the use of two or more panes of glass separated by a spacer bar, creating a sealed unit.
This design introduces a range of benefits that address the limitations of single glazing, resulting in improved energy efficiency, comfort, and overall performance of windows.
Composition and Design of double glazing
Double glazing consists of two glass panes that are spaced apart and hermetically sealed, often with a layer of insulating gas, such as argon or krypton, between them. The space between the panes acts as a thermal barrier, reducing the transfer of heat between the indoors and outdoors.
Advantages of Double Glazing
Enhanced Insulation
The most notable advantage of double glazing is its superior insulation properties. The air or gas-filled space between the panes acts as a buffer, significantly reducing heat loss during colder months and heat gain during warmer months. This leads to more stable indoor temperatures and reduced reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Noise Reduction
The dual layers of glass and the insulating space contribute to effective noise reduction, creating a quieter and more peaceful indoor environment. This is especially beneficial for homes located in noisy urban areas.
Condensation Control
Double glazing minimizes condensation on the inner pane by maintaining a warmer surface temperature, which reduces the risk of moisture-related issues and mold growth.
Energy Efficiency
The improved insulation provided by double glazing translates into lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills. Homes with double glazing can achieve better energy efficiency ratings and contribute to a smaller carbon footprint.
UV Protection
Some double glazing options incorporate coatings that provide UV protection, reducing the fading and damage caused by direct sunlight to interior furnishings and belongings.
Comfort and Well-being
The consistent indoor temperature, reduced drafts, and enhanced noise control offered by double glazing contribute to a more comfortable and pleasant living environment.
Modern Advancements
Modern double glazing technology has led to further enhancements, such as low-emissivity (low-E) coatings. These coatings are applied to the glass surfaces to reflect heat back into the room while allowing sunlight to enter. This maximizes natural light while minimizing heat loss, contributing to even higher energy efficiency.
Benefits of double glazing compared to single glazing
The transition from single glazing to double glazing brings about a multitude of benefits that significantly improve the performance, comfort, and energy efficiency of windows and, consequently, the entire living environment. By understanding these advantages, homeowners can make informed decisions when choosing between these two window pane options.
Enhanced Insulation
One of the most notable benefits of double glazing is its superior insulation capabilities. The air or gas-filled space between the panes acts as a barrier against heat transfer, effectively reducing heat loss during colder months and heat gain during warmer months. This results in more stable indoor temperatures, minimizing the need for constant heating and cooling. In contrast, single glazing offers minimal insulation, leading to temperature fluctuations and increased energy consumption.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Double glazing significantly contributes to improved energy efficiency in homes. By reducing the reliance on heating and cooling systems to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, homeowners can experience substantial energy savings. Lower energy consumption not only leads to reduced utility bills but also aligns with sustainable practices and environmental conservation.
Noise Reduction
Double glazing excels at noise reduction, providing a quieter indoor environment. The combination of two glass panes and the insulating space in between helps dampen external noises, making it an ideal choice for homes situated in noisy urban areas, near highways, or close to commercial zones. Single glazing, on the other hand, offers limited noise insulation, allowing outdoor sounds to penetrate more easily.
Condensation Control
Double glazing minimizes the occurrence of condensation on the inner pane, as the insulating layer helps maintain a warmer surface temperature.
This reduces the risk of moisture-related issues such as mold growth and potential damage to window frames. Single glazing, due to its colder inner surface, is more prone to condensation, which can lead to problems over time.
Comfort and Well-being
The enhanced insulation, noise reduction, and condensation control provided by double glazing contribute to a higher level of indoor comfort and well-being. Occupants can enjoy a more consistent and pleasant living environment, free from temperature fluctuations, drafts, and intrusive noise.
UV Protection
Certain types of double glazing incorporate coatings that offer UV protection. These coatings help block harmful ultraviolet rays from entering the home, reducing fading and damage to interior furnishings, flooring, and artwork. Single glazing provides minimal UV protection, which can lead to accelerated deterioration of indoor materials.
Types of Double Glazing
Double glazing, with its innovative design of two glass panes separated by an insulating gap, has evolved to offer a variety of specialized options that cater to different needs, climates, and preferences.
These variations in double glazing provide homeowners with enhanced levels of insulation, energy efficiency, and performance. Let’s explore the different types of double glazing and their unique characteristics:
Standard Double Glazing
Standard double glazing consists of two glass panes separated by an air gap. This classic design offers improved insulation compared to single glazing by creating a barrier that reduces heat transfer.
While it provides a basic level of energy efficiency and noise reduction, additional advancements have led to more specialized options.
Low-E (Low Emissivity) Coating
Low-E double glazing features a microscopically thin, virtually invisible coating on one of the glass panes.
This coating reflects heat back into the room while allowing sunlight to pass through. In colder climates, Low-E coatings help retain indoor warmth, while in warmer climates, they reduce heat gain. This type of double glazing enhances energy efficiency by further minimizing heat loss and heat gain.
Gas-Filled Double Glazing
In this type of double glazing, the insulating gap between the glass panes is filled with a dense, inert gas such as argon or krypton. These gases have lower thermal conductivity than air. As a result, they create a barrier that effectively reduces the transfer of heat between the indoor and outdoor environments. Gas-filled double glazing provides improved thermal performance and energy efficiency, making it a popular choice for climates with extreme temperature variations.
Choosing Between Argon and Krypton
When opting for gas-filled double glazing, homeowners have a choice between two insulating gases: argon and krypton.
Each gas offers distinct advantages and considerations, impacting factors such as insulation, cost, and overall window performance.
Argon Gas
Argon is the more commonly used gas in gas-filled double glazing. It is cost-effective and provides a notable improvement in insulation compared to air-filled gaps.
Argon’s thermal conductivity is lower than that of air, which means it reduces heat transfer more effectively.
While not as efficient as krypton, argon strikes a balance between enhanced insulation and affordability. It is well-suited for regions with moderate climate conditions and offers a tangible improvement over standard air-filled double glazing.
Krypton Gas
Krypton is a premium option that offers even higher insulation properties than argon. With its significantly lower thermal conductivity, krypton creates a more effective barrier against heat transfer.
This makes it ideal for regions with extreme climate conditions, where maintaining stable indoor temperatures is crucial.
However, the enhanced insulation comes at a higher cost compared to argon. Krypton is especially beneficial for homeowners who prioritize top-tier energy efficiency and are willing to invest in the technology.
Considerations
When choosing between argon and krypton for gas-filled double glazing, several factors should be taken into account:
Climate: Consider the local climate and temperature variations. Krypton is more suitable for extreme climates with harsh winters and hot summers, while argon offers a cost-effective solution for milder climates.
Budget: Krypton is more expensive than argon. Homeowners should assess their budget and determine whether the higher cost of krypton aligns with their energy efficiency goals.
Energy Savings: While both gases contribute to energy savings, krypton offers slightly higher efficiency. Homeowners seeking maximum energy savings may opt for krypton, especially in climates where insulation is a primary concern.
Window Design: The overall design and specifications of the windows, including the width of the air gap and the quality of the window frame, can also influence the choice of gas.
Choosing between argon and krypton for gas-filled double glazing involves a trade-off between enhanced insulation and cost.
Argon offers a good balance of performance and affordability, making it a suitable choice for many homeowners. Krypton, on the other hand, provides premium insulation but comes with a higher price tag.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on factors such as climate, budget, and energy efficiency priorities, ensuring that the chosen gas aligns with the specific needs and goals of the homeowner.