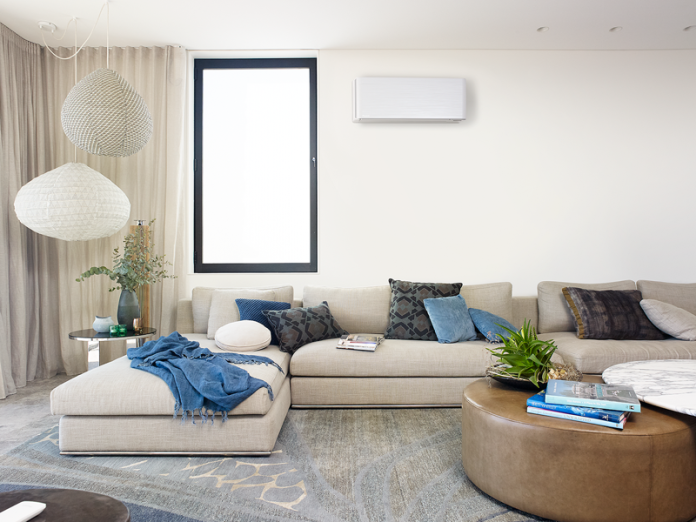
Standalone air conditioners are widely used to create a comfortable microclimate. First of all, it is explained by the low cost of purchasing HVAC in Houston and relatively easy installation, as well as low noise level, compactness, variety of designs, and consumer functions. Structurally, air conditioners can be in the form of a monoblock or several separate units. Usually, such conditioners are able not only to cool air but also to heat, dehumidify, and in some cases, humidify it.
How Much Energy Does a Conditioner Consume?
Sometimes you can find claims that air conditioners consume a lot of energy. This estimation is very superficial and groundless. The work of an air conditioner, its energy consumption, and energy efficiency depend on many factors:
- The capacity of the air conditioner;
- Area of an air-conditioned room;
- The temperature outside;
- Heat insulation of the premise;
- Proper installation, wiring, and adjustment of the air conditioner.
The cooling and heating capacity of different models is usually in the range of 2-10 kW. According to the way of controlling the cold-productivity, air conditioners are subdivided into standard (two-step control by switching on and off the compressor) and inverter (step-by-step control by changing the speed of the compressor and fans).
Modern air conditioners are most often inverters, which allows for maintaining more comfortable conditions indoors and saving energy. They are complicated technical products with microprocessor automatics and high pressure in the refrigerating circuit. Estimated service life (10-12 years), claimed by most manufacturers, can be provided only with proper installation and carrying out further technical (service) maintenance.
Characteristics of the Air Conditioner According to the EER and COP Efficiency Scale
For cooling and heating modes, respectively, for clarity, instead of the concept of COP, the energy efficiency scale of air conditioners has been introduced:
- EER (effective cooling capacity) – the ratio between the electricity consumed and the cooling capacity of the air conditioner. In this case, it is estimated by the cooling capacity that the air conditioner delivers at maximum load.
- COP (effective heating capacity) is the ratio between the electric power consumed and the heating capacity of the air conditioner. The same as in the case with EER, the heating capacity, which the air conditioner can develop at full load, is estimated.
For convenience, these indicators are divided into 7 categories and denoted by Latin symbols A-G, which correspond to the energy efficiency value of cooling or heating. As the characteristics of air conditioners and their energy efficiency are constantly improving, new standards have recently been adopted to classify the best energy efficiency values above class “A” – they are “A+”, “A++” and “A+++”. This classification affects all household appliances. Today, most of the electrical appliances sold in developed countries have an energy efficiency class higher than “A+”.