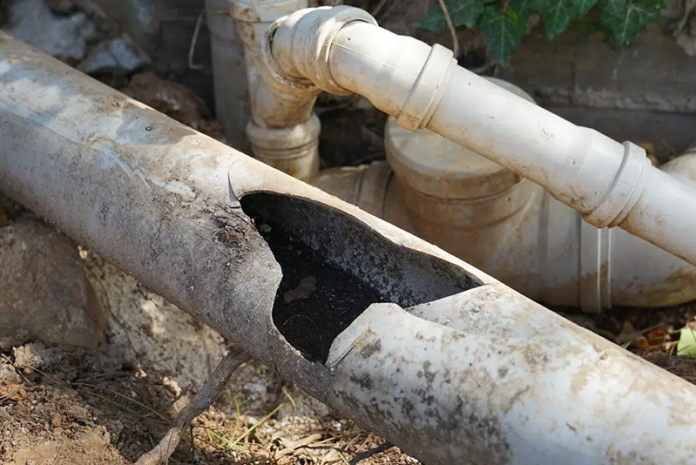
Transporting water, gas, oil, and other fluids in pipes is crucial for our infrastructure. As important as they are for various purposes, their maintenance is also equally important. Pipes are already prone to damage and degradation, which is a concerning issue. Formation of cracks in pipes is a common issue, which causes leaks, structural damage and environmental hazards. Also, the high cost of repairs, time and effort to find a reliable plumber from Anaheim seems a bit much.
This blog walks through the various causes of crack formation in pipes, and its preventive and mitigation strategies to address the issue.
Causes of Cracks in Pipes
- Corrosion
It is a silent culprit for causing pipe cracks. When pipe material reacts with environmental factors, the surface starts deteriorating. These factors include water, chemicals, and corrosive substances of the transported fluids. Corrosion weakens the pipe material over time and builds cracks.
Corrosion occurs in two forms: Uniform and Localized.
Uniform corrosion occurs evenly across the pipe’s surface. It makes the pipe walls thinner over time, which causes cracks easily. Localized corrosion, on the other hand, forms pits that eventually evolve into cracks.
- Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC)
It is a particular form of crack which is corrosion-induced.
It occurs under tensile stress in the presence of a corrosive environment. It is more destructive as it can lead to rapid crack propagation, making pipes susceptible to sudden failure. The type of material and environmental conditions influence the stress corrosion cracking. Keeping in mind these factors is crucial for the prevention of such cracking.
- Freezing Temperature
During the colder months of the year, pipe cracks or bursting are common. The colder temperature causes the water inside to freeze. The frozen water or ice formed expands in the pipe, causing pipe bursts that allow large amounts of water to fill an area, causing water damage. This situation is common in winter and needs a quick remedy from a nearby plumber in Anaheim.
- Mechanical Damage: External Forces Responsible for Pipe Cracks
External forces include physical forces that lead to crack development in pipes. Physical impacts, excessive bending or flexing, vibrations, and damage during installation, maintenance, or excavation activities can all cause structural damage. Careful handling is essential during installation and related activities to reduce the risk of cracks.
- Fatigue
Repeated cycles of stress and fluctuation in pressure induce fatigue that gradually leads to crack formation in pipes. Temperature variations and high-pressure applied increase fatigue.
- Thermal Stress
Cracks in pipes occur if changes in the temperature are rapid. It causes thermal stress. Significant variations in temperature cause contraction and expansion. Excessive fluctuations stresses the pipe material. This develops cracks, especially in materials with poor thermal conductivity.
- Material Defects
Poor manufacturing or material quality can introduce inherent defects in pipes. These defects may include microstructural flaws or impurities in the material. Over time, these weaknesses can develop into cracks, making material quality a critical factor in pipe longevity.
- Chemical Attack
The reaction induced by an aggressive chemical causes a corrosive reaction inside the pipe. This reaction weakens the structure gradually and makes it susceptible to cracking. Industrial wastewater often has corrosive chemicals that can cause cracks. Pipes with corrosion-resistant coatings can prevent such attacks.
- Aging
Pipes, like all infrastructure, undergo natural aging processes over time. As pipes age, they may become more susceptible to cracking, due to factors like material aging, fatigue, and changing environmental conditions. The gradual degradation of the pipe material can lead to a loss of structural integrity, making it more prone to cracks.
- Welding Defects
Defects in the weld or improper welding techniques make the pipes prone to cracking. Common defects include incomplete penetration, lack of fusion, porosity, and cracks within the weld. These defects can compromise the overall integrity of the pipe.
- Installation Defect
While there could be defects in the material of the pipe or environmental factors that cause cracks in pipes, plumbers or technicians handling the installation could also be at fault. Pipe installation is a sensitive step, where careful handling, spacing, optional cutting and welding affect the working. A little negligence may make the pipe susceptible to damage.
Preventive Measures for Cracks in Pipes
- Material Selection
The selection of the right material makes a pipe powerful and acts as the first line of defense against pipe cracking. Factors, such as, the corrosivity of the transported fluid, temperature, and mechanical stresses should be considered, before choosing pipe materials. To extend the lifespan of pipes, utilize corrosion-resistant materials and alloys.
- Corrosion Protection
Implementing corrosion protection measures is crucial for preventing corrosion-related cracking. Coatings, linings, and cathodic protection systems can shield pipes from corrosive environments. Regular inspections and maintenance of these protective measures are essential to ensure their effectiveness.
- Stress bearing capacity
During the pipe design phase, stress analysis can help identify the stress concentration points, and accordingly, changes in the material can be made to make it stronger. Checkpoints for load and pressure can be kept to determine the stress-bearing capacity. Proper design and reinforcement in critical areas can reduce the risk of stress-induced cracking.
- Monitoring and Inspection
Regular monitoring and inspection of pipes are essential for detecting cracks and defects early on. Non-destructive testing techniques, such as ultrasonic and radiographic testing, can be employed to assess the integrity of pipes without causing damage.
- Proper Installation
Careful handling and proper installation techniques are essential to prevent mechanical damage during the construction and maintenance of pipelines. Best industry practices should be known and followed to reduce the risk of cracking and other structural issues.
- Maintenance and Repair
Scheduled maintenance and timely repair of pipes are critical for preventing minor issues from escalating into major problems. Promptly addressing corrosion, erosion, or any other damage can extend the service life of pipes.
- Material Quality Control
Ensuring the quality of pipe materials through stringent quality control measures during manufacturing is essential. Minimizing material defects from the outset can significantly reduce the likelihood of cracks forming in pipes.
Mitigation Strategies for Pipe Cracks
1. Repairs
Repair methods, such as welding, clamping, or application of composite materials are used to reinforce and seal the cracks. The choice of repair method depends on the type and severity of the crack.
2. Pipeline Monitoring Systems
Advanced Pipeline Monitoring Systems use sensors and data analytics to provide real-time information about the condition of pipes. It is a great help for the early detection of issues and gives ample time to take preventive measures before cracks become critical.
3. Rehabilitation and Replacement
Replacement is best in case of severe cracks in pipes. A qualified plumber can help with relining pipes, installing new sections, or even replacing the entire pipeline. Proper planning and execution are crucial to minimize downtime and costs associated with rehabilitation or replacement.
Conclusion
Cracks in pipes can be induced by factors that may be corrosion, mechanical stress, temperature variation and material quality. To ensure the longevity of pipelines and crack prevention, implement preventive measures and mitigation strategies. The raw material used should be given more importance, specifically for its tensile strength and corrosion resistance.
Conducting regular inspections by a qualified plumber in Anaheim and addressing the issue promptly, can minimize the risk of pipe cracks. It also saves the cost of infrastructure repair and prevents excavation activities.